How to Properly Find Derivative: Effective Methods You Need to Know
Understanding how to **find the derivative** is essential for anyone studying calculus. Derivatives play a critical role in mathematics, especially in topics such as **differentiation**, **optimization**, and more. This article will explore effective methods to find derivatives, covering key concepts, rules, and practical applications. Whether you’re a beginner or someone looking to refine your skills in calculus, these insights will be invaluable in navigating this fundamental topic.
Understanding Derivative Basics
Before diving into methods for **finding derivatives**, it’s crucial to grasp the basic concepts. A **derivative** represents the rate of change of a function concerning a variable. In essence, it measures how steeply a curve rises or falls at a particular point, providing insight into the behavior of a function. The foundational formula for the **derivative of a function** involves limits, expressed mathematically as:
f'(x) = lim (h → 0) [(f(x + h) – f(x)) / h]
Finding derivatives can initially seem daunting, but once you comprehend the underlying principles, it becomes significantly more manageable. For example, the **first derivative** indicates the slope of the **tangent line** at a given point on the graph of the function, while the **second derivative** assesses the curvature, revealing information about **concavity** and potential **inflection points**. Understanding these concepts is the backbone of effective differentiation.
Derivative Definition and Notation
When we speak of derivatives, we often refer to various notations you’ll encounter in calculus. The most common forms include **Leibniz notation** (dy/dx) and **Newton notation** (f’). These symbols provide clarity in expressing rates of change and facilitate discussions about derivatives across different mathematical contexts. Each notation serves a unique purpose, allowing you to describe a **differentiable function** within its applicable framework.
Common Derivative Rules
Mastering the **derivative rules** is key to simplifying your calculations. Some of the primary rules include:
- Power Rule: If f(x) = x^n, then f'(x) = nx^(n-1).
- Product Rule: If f(x) = g(x) * h(x), then f'(x) = g(x) * h'(x) + g'(x) * h(x).
- Quotient Rule: If f(x) = g(x)/h(x), then f'(x) = (g'(x)*h(x) – g(x)*h'(x))/[h(x)]^2.
Employing these rules not only streamlines the process of finding derivatives but also aids in tackling complex functions effectively.
Introduction to Higher Derivatives
In calculus, once you’ve mastered the **first derivative**, you can explore **higher order derivatives**. These derivatives can provide deeper insight into the function’s behavior. The **second derivative** can indicate changes in the slope (concavity) and help find **local extrema**. In this manner, **higher derivatives** lead to a more profound understanding of function behavior, particularly when analyzing functions in optimization problems or assessing critical points.
Techniques for Differentiation
Finding derivatives can be tweaked with different techniques. Understanding **differentiation techniques** will render you more capable of handling diverse problems. One powerful technique is the **chain rule**, primarily useful when computing the derivative of a composite function. The chain rule states:
If f(x) = g(h(x)), then f'(x) = g'(h(x)) * h'(x).
This expression highlights how to relate derivatives of combined functions. By applying this method, you can simplify the process of finding the **derivative** for multi-faceted functions effectively.
Implicit Differentiation
Another critical technique is **implicit differentiation**, often employed when dealing with relationships where y isn’t isolated. For example, if you have an equation like x^2 + y^2 = 1, where y and x are intertwined, differentiating both sides with respect to x (and labeling dy/dx when encountering y) can help you find y’. This approach maintains the connection between variables without breaking their relationship by rearranging them individually.
Application in Real-Life Scenarios
The **applications of derivatives** extend to numerous fields, such as physics and economics. For instance, in physics, a **derivative** can represent velocity (the first derivative of position with respect to time) and acceleration (the second derivative). Understanding how to **find derivatives** and visualizing their significance can thus offer invaluable insights into real-world dynamics.
Economists utilize **derivatives** to assess marginal cost and revenue, offering nuanced understanding relative to productivity and cost efficiencies. These real-life applications illustrate the critical role of derivatives beyond abstract mathematics, bringing calculus concepts to life.
Computational Tools and Resources
Thanks to advancements in technology, several resources can aid in the differential process. A popular tool is the **derivative calculator**, which can swiftly evaluate complex derivatives for you, allowing for quick verification of your manual calculations. However, while these tools are advantageous, it’s essential to develop foundational skills in **computing derivatives** manually for a comprehensive understanding of calculus principles.
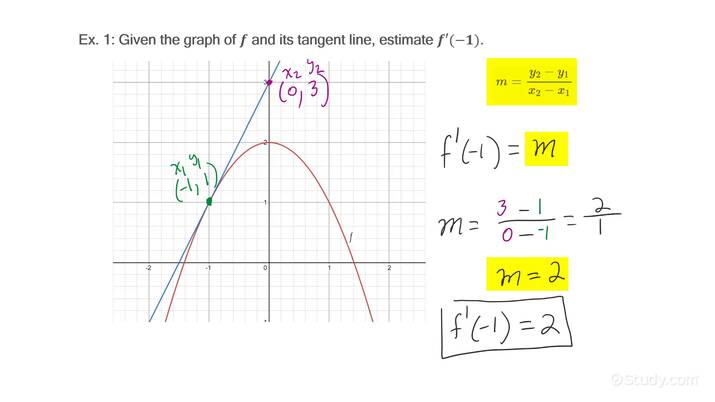
Graphical Representation of Derivatives
Graphically representing derivatives can enhance understanding significantly. Plotting the function alongside its **derivative** can clarify the relationship between a function and its slope. This visualization aids in intuitively grasping important concepts like **local extrema** or inflection points where the curvature changes. Technology, such as graphing calculators and software, can help demonstrate these principles more effectively.
Learning Resources for Mastery
Online platforms and educational websites can be invaluable in learning **calculus concepts** and practical applications of derivatives. Video tutorials can provide step-by-step guides on how to use various **differentiation techniques** effectively. Furthermore, practicing through derivative quizzes and engaging with interactive calculus environments aids retention and fosters a deeper understanding of derivatives in multiple contexts.
Key Takeaways
- A solid understanding of the basic rules of differentiation is fundamental for finding derivatives effectively.
- Employing visualizations and real-life applications of derivatives can greatly enhance comprehension.
- Utilizing computational tools complements foundational learning but should not replace manual problem-solving skills.
- Exploring higher derivatives offers deeper insights into function behaviors, particularly in optimization contexts.
- Utilize diverse learning resources to solidify your understanding and application of derivative concepts.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of the second derivative?
The **second derivative** is crucial as it indicates the rate of change of the first derivative. This means it provides insights into the **concavity** of the function and can help identify **inflection points** where the function changes from concave up to concave down or vice versa. It also plays a key role in determining local maxima and minima in optimization problems.
2. How can I find partial derivatives of multivariable functions?
To find **partial derivatives**, hold all variables constant except for the one you’re differentiating with respect to. Use traditional derivative rules where applicable. This is especially useful in functions with multiple inputs, enabling the analysis of how one variable affects the overall function while disregarding the influence of others.
3. Which derivative rules should I prioritize when learning?
Start with the **power rule**, **product rule**, and **quotient rule**. These foundational rules will help you handle most derivative problems. Once you feel confident, delve into more advanced techniques such as the **chain rule** and **implicit differentiation**. Gaining proficiency in these areas will significantly streamline your calculus journey.
4. What role do derivatives play in optimization problems?
Derivatives are instrumental in optimization problems as they enable the identification of **critical points** where the function’s value might reach a maximum or minimum. By calculating the **first derivative** and setting it to zero, you can find these points. Using the **second derivative test** further clarifies the nature of these critical points, ensuring effective optimization strategies.
5. Can you visualize derivatives effectively?
Yes, **graphical representations** of functions and their corresponding derivatives provide a clear understanding of the slope at any given point. Plotting the function and its derivative together significantly enhances your grasp of the relationship between them, allowing you to visualize **local extrema** and inflection points seamlessly.
By understanding just how to **properly find derivatives**, you equip yourself with essential tools for success in calculus and beyond. Whether it’s for academic pursuits, real-world applications, or advancing your knowledge, derivatives represent a multifaceted topic essential for many disciplines.