How to Effectively Calculate Percent Yield: Essential Guide for 2025
Understanding how to calculate percent yield is crucial for anyone engaged in chemical reactions, whether in a professional laboratory setting or in educational contexts. This guide explores the core concepts like the percent yield formula, practical applications, and common challenges faced while conducting these calculations. We will break down the percent yield definition, exemplify how to derive the theoretical yield and actual yield, and provide practical tips on improving these metrics in laboratory settings.
The Basics of Percent Yield Definition
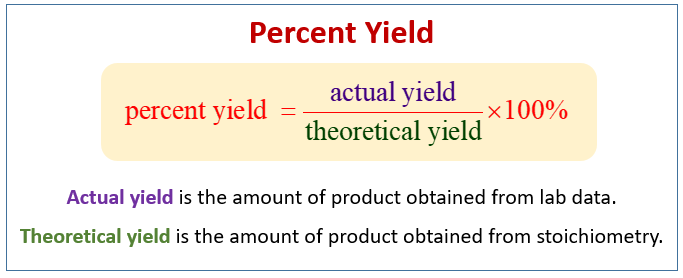
At its core, the percent yield definition refers to the efficiency of a chemical reaction, expressed as the ratio of the actual yield obtained from an experiment to the theoretical yield predicted by stoichiometric calculations. The formula for calculating percent yield is straightforward:
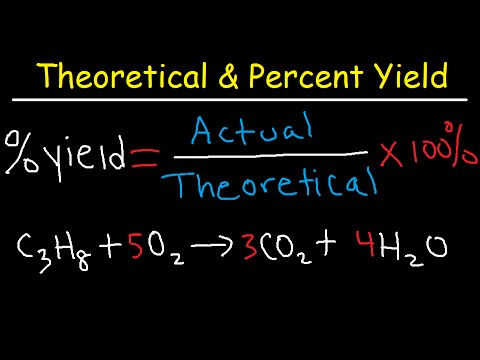
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100%. This equation illustrates how effectively reactants have been transformed into products during a reaction. If reactants do not fully convert into desired products, the yield percentage will be low, indicating inefficiency in the reaction process.
The Role of Theoretical Yield in Calculations
The theoretical yield represents the maximum amount of product that can be formed from given amounts of reactants, based on balanced chemical equations. It is calculated using the mole ratios from the balanced equation and the initial amounts of reactants. For example, in a reaction where hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water, if you start with 2 moles of hydrogen and 1 mole of oxygen, the theoretical yield will be based on this 2:1 ratio.
Accurate calculations of the theoretical yield are crucial since they form the basis for determining the percent yield. Any miscalculations may lead to inaccurate assessments of reaction efficiency.
Practical Example of Percent Yield Calculation
To exemplify this concept, let’s consider a chemical reaction in which 50 grams of a reactant produces 40 grams of the desired product under ideal conditions. Here’s how to calculate the percent yield:
- Determine the theoretical yield, which we will say is 50 grams for this example based on calculations.
- Plug the values into the percent yield formula: Percent Yield = (40g / 50g) × 100% = 80%.
This calculation illustrates that 80% of the products were formed relative to the maximum expected yield, emphasizing the importance of knowing both the actual and theoretical yields.
Understanding Factors Affecting Percent Yield
Several factors can significantly affect the percent yield in reactions. Identifying and controlling these factors can lead to improved outcomes in chemical experiments.
Common Factors Leading to Low Percent Yield
There are various reasons why a reaction may yield less product than expected. Some common factors include:
- Incomplete reactions: Not all reactants may convert into products due to kinetic barriers or thermodynamic stability.
- Side reactions: Unexpected reactions might convert some of the desired product into unwanted byproducts, reducing the actual yield.
- Experimental errors: Human errors in measurement or procedural errors can lead to inaccuracies in the yield calculations.
Strategies for Improving Percent Yield
To optimize the yield efficiency, consider adopting the following strategies:
- Optimize reaction conditions: Adjusting temperature, pressure, or concentration can lead to higher product formation.
- Minimize side reactions: Use purification techniques to remove byproducts and ensure more reactants go toward desired products.
- Careful measurements: Use precise scales and instruments to minimize errors that can impact actual yield assessments.
Significance of Calculating Percent Yield in Chemistry
Understanding percent yield holds considerable significance in both academic and industrial chemistry. It reflects the efficiency of a reaction and helps researchers and experimenters gauge the viability of a synthetic pathway or a process.
Applications of Percent Yield Assessments
In a laboratory, tracking the percent yield accuracy can contribute to several important aspects:
- Quality control: Regularly assessing percent yield can identify issues in manufacturing processes.
- Cost efficiency: Higher yields equate to less wastage of reactants, significantly lowering costs.
- Research hypothesis validation: Adjusting reaction conditions based on plant yield can validate or refute scientific hypotheses.
TRend Comparisons: Assessing Yield Over Time
By calculating and monitoring percent yield, companies and researchers can establish benchmarks for future experiments, leading to cumulative improvements in processes over time. For example, a lab might discover over several experiments a gradual drop in yield due to aging reactants, prompting action to either enhance reactant quality or adjust procedures.
Practical Tips for Percent Yield Analysis
Enhancing your skills in calculating percent yield means knowing how to efficiently analyze data and apply theories practically. Below are essential tips for conducting accurate yield analysis in labs:
Establishing Accurate Baselines
Before starting tests, be aware of the expected theoretical yield based on similar experiments. Conduct thorough empirical studies if undergoing a completely new reaction, document your gathered data, analyze variances, and compare against known yield metrics.
Formulate Detailed Protocols
Providing clear guidelines that showcase protocols is essential for yielding consistency in results. This includes chemical preparation methodologies, time frames for reactions, and stepwise instructions for measuring yields. By reducing variability in processes, you maintain a degree of control that greatly impacts your yields.
Also, incorporate precautions to prevent human errors during measurements, ensuring that your percent yield calculations remain reliable.
Conclusion: Mastering Your Percent Yield Calculations
In summary, mastering percentage yield calculations isn’t merely about knowing percent yield formulas—it’s about grasping the broader picture of efficiency and effectiveness in chemical reactions. By understanding how various conditions impact yield, implementing exacting measurements, and optimizing the methodologies, you can overcome the challenges of laboratory practices. With this practical guide, you’re better equipped to refine your chemical techniques and elevate your productions.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the foundational definitions of percent yield is essential in chemistry.
- Improving yield can significantly influence cost and quality control in laboratory practices.
- Implementing precise techniques and optimized strategies allows for more accurate yield calculations.
- Continuous assessment and adjustments based on yield results can further bolster efficiency.
FAQ
1. What is the importance of categorizing yield types?
Categorizing yield types, such as high percent yield and low percent yield, allows chemists to identify patterns that influence efficiency. Understanding these types is crucial when making adjustments to reaction conditions.
2. How can laboratory conditions impact yield?
Laboratory conditions such as temperature, pressure, and reactant concentrations directly affect percent yield. Ensuring optimal settings can significantly improve reaction efficiency and yield results.
3. What methods can be used to optimize yield?
Methods to optimize yield might include recalibrating reaction conditions, purifying reactants, or removing side byproducts, all aimed at maximizing the final production of the desired product.
4. Are percent yield calculations different in industry vs. research?
While the fundamental calculations remain the same, industry focuses on high-volume, consistent yields for cost-efficiency, whereas research is more exploratory, often accepting lower yields to validate new hypotheses.
5. How do you handle unexpected low yields?
Investigate the potential causes, such as experimental error, incomplete reactions, or incorrect stoichiometry. Systematically adjusting those variables based on collected data can help recover expected yields in subsequent iterations.