How to Read an EKG: Essential Techniques for Modern Healthcare in 2025
Understanding how to read an EKG (electrocardiogram) is crucial for healthcare professionals in detecting and diagnosing cardiac conditions. As we move into 2025, the ability to interpret EKGs efficiently enhances patient outcomes and equips medical providers with essential skills. In this article, we will cover fundamental techniques for EKG interpretation, key terminology, common EKG abnormalities, and insightful practices for accurate readings. Our goal is to prepare you for modern EKG analysis using innovative tools and strategies.
The Basics of EKG Interpretation
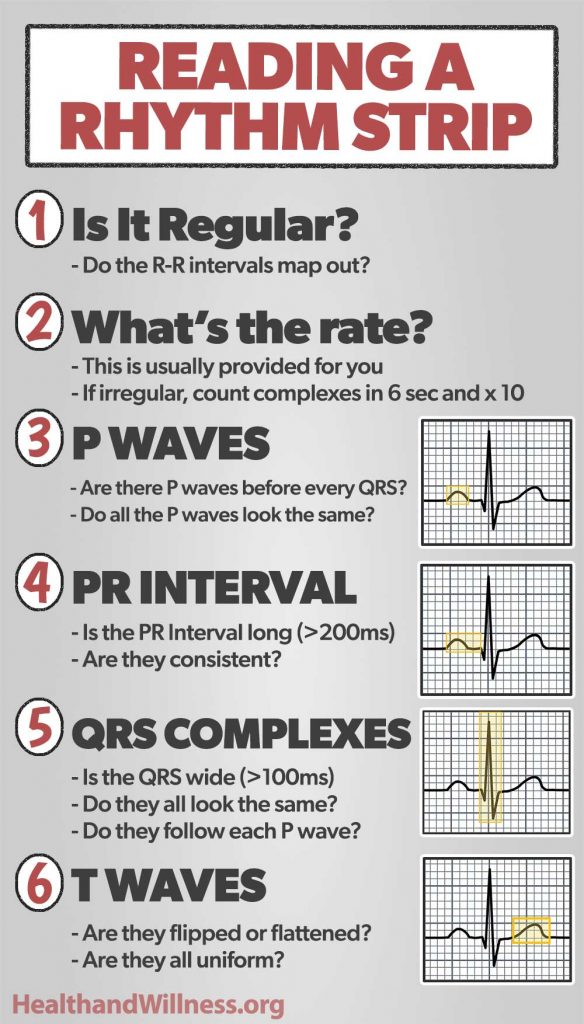
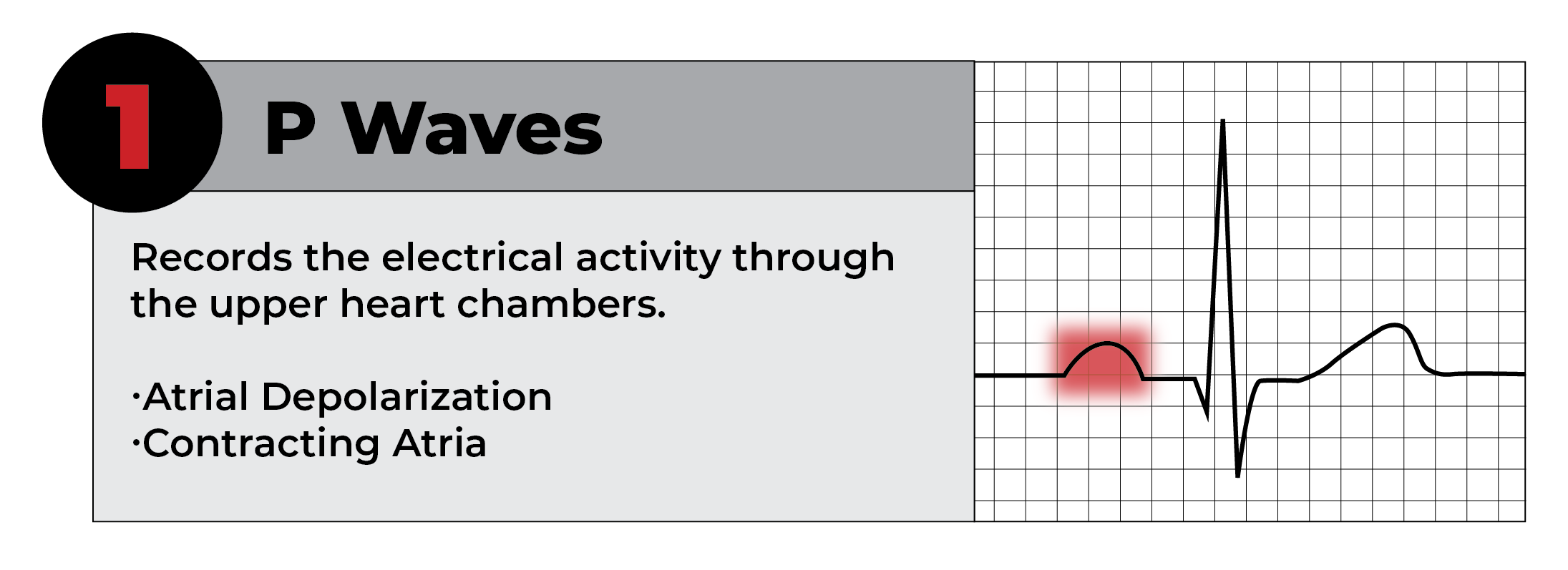
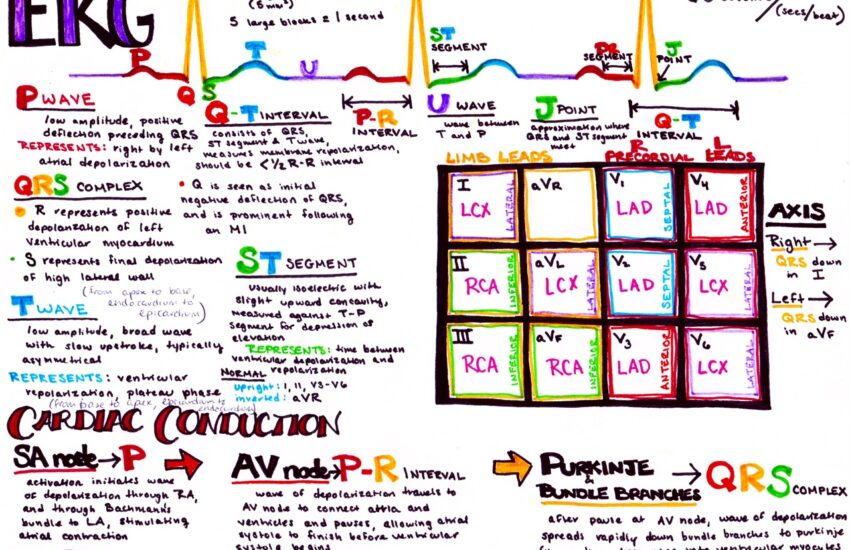
To begin your journey in understanding EKG, it is essential to familiarize yourself with EKG basics. An EKG strips reveal the heart’s electrical activity through a graph, commonly displayed on paper or a digital screen. EKG interpretation relies on accurately identifying typical cardiac rhythms, assessing waveforms, and understanding the significance of PQRST complexes within the tracing. Each component of the pad holds critical information; the P wave signifies atrial depolarization, while the QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization.
Understanding EKG Waves
One of the most vital aspects of reading EKG strips is the comprehensive understanding of EKG waves such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. Each waveform corresponds to specific phases of cardiac activity. The distance, shape, and amplitude provide valuable information on heart function. For example, an elongated QRS complex may signify a delay in ventricular conduction, indicating possible underlying issues such as bundle branch block or ventricular hypertrophy.
EKG Electrode Placement and Lead Configuration
Proper EKG electrode placement is crucial for accurate readings. Developers of modern EKG devices provide guidelines to ensure successful attachment of leads, improving signal clarity. Commonly used configurations include limb leads and precordial leads, which help in mapping different heart regions. Incorrect placement may lead to artifacts and misinterpretations, hindering clinical decision-making.
Common EKG Abnormalities and Their Significance
Identifying EKG abnormalities is fundamental in proactive cardiac care. Clinicians must be proficient in diagnosing conditions based on EKG findings, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia. Subtle changes in waveform morphology or timing can indicate significant clinical implications, making awareness of abnormal presentations essential.
Recognizing Arrhythmias and Cardiovascular Diseases
Each EKG tracing carries profound significance. Recognizing arrhythmias such as atrial flutter and bradycardia on EKG is vital for timely management. These conditions, if unrecognized, may lead to serious complications, requiring immediate intervention. An EKG interpretation guide can assist professionals in distinguishing between normal and pathological findings in complex scenarios.
ST Segment Changes and Their Clinical Relevance
ST segment changes often indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction. Assessing the elevation or depression of this segment on the tracing can help determine the severity of the cardiac event. Emergency professionals rely on this information for swift treatment, showcasing the importance of emergency EKG interpretation services in acute care settings.
Practical Steps for Accurate EKG Reading
Interpreting EKGs accurately necessitates knowledge, practice, and a systematic approach. A step-by-step checklist can streamline the process, ensuring no detail is overlooked. Begin by examining the rhythm and heart rate calculation, recognizing the presence of normal EKG patterns.
Heart Rate Calculation Techniques
One effective way of calculating heart rate involves counting the number of R-R intervals in a six-second strip and multiplying it by ten. This method helps quickly estimate the patient’s heart rate, which is crucial in diagnosing conditions like tachycardia or bradycardia. Understanding normal heart rhythms aids in differentiating between sinister alterations indicative of disease.
Analyzing QRS Complex and T Wave Abnormalities
QRS complex analysis is essential in evaluating bundle branch blocks and potential fibrosis. Similarly, monitoring T wave abnormalities can signal electrolyte disturbances or medication effects. Both of these analyses contribute context to the overall interpretation of the EKG, forming a comprehensive picture of the patient’s cardiovascular health.
Innovations in EKG Monitoring and Education
As technology advances, so do our approaches to EKG monitoring. Today’s healthcare professionals often benefit from EKG software tools, capable of analyzing traces and providing real-time feedback. Moreover, EKG education strategies, such as electronic training modules and virtual workshops, equip new nurses and technicians with essential skills as they artfully teach EKG techniques.
Holter Monitoring: A New Era in EKG Technology
Holter monitoring, a method of continuous EKG monitoring, is particularly useful in capturing transient arrhythmias. This method records heart data over 24-48 hours, providing invaluable insight into abnormal rhythms that might not appear on a standard EKG. Its application highlights the important role of continuous monitoring in outpatient settings and long-term cardiac care management.
Educational Resources and Training Opportunities
Today, multiple resources are available for EKG for beginners. From online guides to immersive workshops, aspiring technicians can gain confidence and competence in interpreting EKGs through structured learning. The role of peer-reviewed material and evidence-based EKG analysis can significantly enhance one’s ability in practical, real-world application.
Key Takeaways
- Mastering the fundamentals of EKG interpretation is vital for healthcare professionals.
- Regular practice and familiarity with EKG basics lead to improved accuracy and confidence in readings.
- Understanding and recognizing EKG abnormalities brandishes more effective treatment strategies.
- Continuous education and use of modern technology equip staff with enhanced EKG interpretation skills.
- Engaging in collaborative learning and professional development solidifies knowledge retention and practical application.
FAQ
1. What role does artifact recognition play in EKG interpretation?
Artifact recognition allows professionals to isolate inaccuracies in an EKG tracing due to extraneous factors. Common artifacts include muscle interference and electrical noise, affecting waveform clarity. Awareness of these artifacts ensures accurate diagnosis and prevents misinterpretation with serious clinical consequences.
2. How does the placement of EKG electrodes affect readings?
Patient preparation for EKG and the precise placement of EKG electrodes significantly influences output quality. Incorrectly situated electrodes lead to distorted or misleading data, disguised as arrhythmias or other abnormalities, hampering effective assessment of heart function. Adhering to correct configuration protocols is paramount.
3. Can EKGs help assess heart rate variability?
Yes, using standard EKG analysis, healthcare professionals can effectively evaluate heart rate variability, a crucial marker for assessing autonomic functions. Variability reflects changes in heart rhythm relating to stress, health conditions, and overall fitness levels, providing a holistic view of patient wellness.
4. Why is understanding EKG waves important in clinical practice?
Understanding EKG waves is vital for clinicians, as they directly relate to the electrical activities of the heart, indicating functionality and overall cardiovascular health status. Recognizing these waves directly informs patient care decisions, differentiating between normal and pathological physiological responses.
5. What innovations in EKG technology should healthcare providers consider?
Healthcare providers should explore remote EKG monitoring and advanced software tools that aid in adapting EKG readings to suit individual patient needs. Innovations also include mobile applications supporting EKG analysis, improving access to critical interpretations in urgent situations, marking an important advancement towards patient-centered care in cardiology.