Growing Grapes: A Comprehensive Guide to Success in 2025
Welcome to your ultimate guide on growing grapes efficiently in your garden or vineyard. As we explore the methods, techniques, and best practices involved in grape cultivation, this comprehensive article will provide you with everything you need to create a flourishing grapevine paradise. Whether you’re planting grape varieties for wine production or home use, this guide will cover all key aspects, from soil preparation to grape harvesting.
Soil Preparation for Grapes
Understanding the importance of proper soil preparation is essential for effective grape growing. The right soil composition contributes significantly to grapevine health, root development, and **grape quality**. Ideally, grapes thrive in well-draining, nutrient-rich soils with a pH level between 6.0 and 6.8. A proper **soil testing for grapes** will provide insights on the nutrient content and pH level, allowing you to amend the soil as needed.
Testing Soil and Amending Nutrients
Start with a **soil test**, which will indicate its nutrient status and pH level. Based on the results, amending the soil with organic matter, such as compost, can greatly improve its structure and fertility. Incorporating specific nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, through organic fertilizers supports the healthy development of your grapevines. Additionally, you might consider adding limestone or sulfur to adjust pH levels if necessary.
Preparing the Planting Site
Selecting the right location for your grapevines is critical. Grapes need full sun exposure for at least six hours daily. Clear the planting site of weeds and debris to ensure optimal conditions. Create raised beds if your soil has drainage issues, and consider using mulching techniques to control weeds and retain moisture.
Choosing Grape Varieties
With over 10,000 registered grape varieties, selecting the appropriate type for your climatic conditions and growing preferences is crucial. Consider factors such as grape climate, susceptibility to diseases, and intended use (e.g., table grapes or wine production). Popular varieties include Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, and Concord for those just starting in their grape-growing journey.
Beginners’ Selection of Grape Varieties
If you are new to grape growing, selecting grape varieties for beginners can set you up for success. Varieties like Reliance and Cascade are known for their resilience and adaptability to various climates. Conduct research on the local growing conditions and market demand for specific grapes to ensure a successful harvest.
Cultivating Cold Hardy Grapes
For gardeners in colder regions, it’s essential to explore cold hardy grape varieties that can withstand harsh climates. Look into varieties such as Marquette and La Crescent, specially bred to survive low temperatures without compromising grape quality.
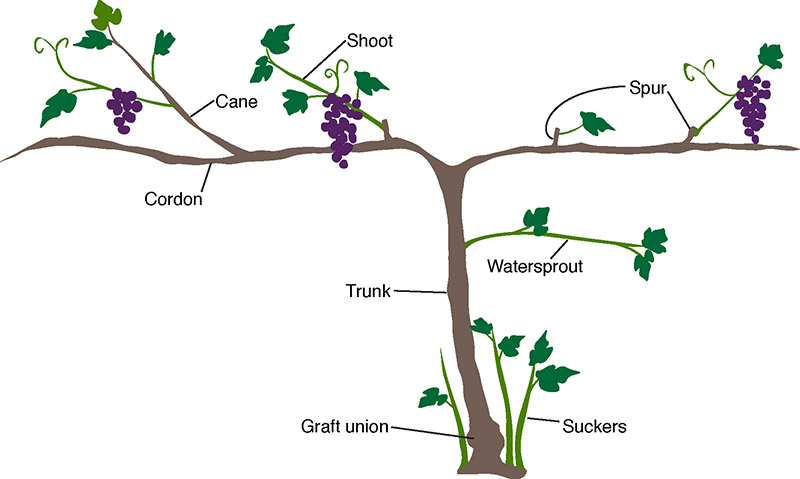
Grape Vine Management Techniques
Effective vine training and care are critical to maximizing yields. Employing proper techniques in canopy management and trellising can help achieve optimal sun exposure and air circulation, which reduces the chances of disease. Let’s delve deeper into vital practices you should embrace for robust grapevines.
Implementation of Trellis Systems
Selecting an appropriate system for trellising grapes allows your vines to thrive. Systems such as Vertical Shoot Positioning (VSP) or Geneva Double Curtain maximize exposed leaf area, which is essential for photosynthesis. The trellising not only helps manage the vine’s growth but also facilitates easier maintenance during grape harvesting.
Pruning Techniques for Grapes
Mastering pruning techniques is crucial for promoting balance between vegetative growth and fruit production. Pruning should be done during the dormant winter months. Remove any dead, injured, or crossing limbs to maintain an open canopy that allows sunlight to penetrate. For optimal results, prune 70-90% of last year’s growth to encourage robust development of fruiting wood.
Irrigation and Nutritional Considerations
In managing your vineyard, understanding grape irrigation and nutrition plays a vital role in supporting vine growth and improving grape yield. Adequate moisture levels during the growing season ensure healthy foliage and fruit development. Here’s what you should know about irrigation and vine nutrition.
Watering Grapes Effectively
Managing water supply is essential for sustaining **grapevines**. Initially, young plants require consistent moisture. An efficient irrigation system for grapes might involve drip irrigation to deliver water directly to the root zone, minimizing weed competition and preventing potential moisture-related diseases. Monitor soil moisture levels, especially during dry spells, and adjust irrigation accordingly.
Grape Fertilization Strategies
Understanding the types of grape fertilizers and their application can enhance vine health. A balanced fertilizer rich in potassium and phosphorus supports stronger root systems, while nitrogen promotes healthy vine growth. It’s important to avoid over-fertilizing, as excessive growth can lead to poorer grape quality and increased susceptibility to diseases.
Addressing Pests and Diseases
Managing pests and diseases is essential for maintaining healthy grapevines. Ensuring sustainable practices through integrated pest management will help protect your crop. Let’s explore effective measures in pest control and disease prevention.
Identifying Grape Diseases
A thorough understanding of common grape diseases is critical. Fungal issues, such as powdery mildew and downy mildew, thrive in humid conditions. Implementing crop rotation and maintaining adequate air circulation among vines are effective practices. Regularly scouting for early signs of disease and employing organic pest control methods can mitigate infestations.
Pest Management Techniques
Effective pest management involves recognizing the life cycles of common grape pests, including aphids and spider mites. Introducing beneficial insects or using organic pesticides can deter these pests while minimizing harm to the vineyard ecosystem. Regular monitoring and employing a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical controls will provide the best defense.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Practices
After all the hard work improving vine health, knowing how to appropriately harvest grapes is crucial. Adhering to proper timing significantly affects the quality of the end product. Read further for strategies on successful grape picking and post-harvest assessment.
Timing the Grape Harvest
Harvesting at the right moment ensures optimal grape maturity and flavor development. Monitor sugar levels, acidity, and tannin maturity as the harvest approaches. Conduct taste tests regularly, as the fruits will evolve in flavor and sugar content leading up to their prime. Generally, grapes should be harvested when they are fully formed and have a pleasant aroma.
Techniques for Grape Picking
Using proper harvesting tools can make the process more efficient and protect the grapes from damage. Hand-picking is still the preferred method for high-quality fruit, allowing you to selectively choose the best grape clusters. For bulk operations, consider mechanized systems that handle grapes gently to minimize bruising.
Key Takeaways
- Conduct thorough soil preparation and testing for optimal growth.
- Choose grape varieties that suit your regional climate and intended use.
- Employ effective vine training and pruning techniques for better yield.
- Manage irrigation and nutrition for vigorous vine health.
- Monitor pests and diseases to maintain a thriving vineyard ecosystem.
- Harvest at the right time for superior grape quality.
FAQ
1. What is the best time to plant grapes?
The best time to plant grapes typically falls in early spring after the last frost, allowing young vines to establish roots before hot summer conditions can arise. In warmer regions, planting in the fall can also be successful, ensuring they get adequate moisture over winter.
2. How can I improve my grape yield?
Improving grape yield involves conditionally perfecting the growing environment through appropriate vine nutrition, ensuring good soil health, proper irrigation, and implementing advanced pruning and training techniques. Regular monitoring for pests and diseases also allows for timely interventions that can safeguard your harvest.
3. What are signs of grape diseases to look out for?
Common signs of grape diseases include spots on the leaves, wilting foliage, and discolored fruit. It’s vital to regularly inspect your vines for these symptoms, especially during humid conditions, to implement effective management strategies swiftly.
4. Can I grow grapes in containers?
Yes, growing grapes in containers is entirely feasible. Select smaller-growing varieties and ensure that your pots have adequate drainage. This is a great option for those with limited space or soil quality issues.
5. What is the role of crop rotation in grape farming?
Crop rotation plays a role in improving soil health and reducing disease incidence in grapes. By alternating the type of crops grown in a specific area, you can enhance soil nutrient levels and break pest cycles, resulting in healthier vines and greater yields.
6. How does climate affect grape growth?
Climate significantly impacts grape growth through regulating temperature, sunlight, and moisture conditions. The right climate ensures grapes achieve optimal grape maturity and can influence flavor profiles and grape quality, thus impacting overall yield.
7. What are sustainable practices for grape growing?
Sustainable practices in grape growing include using organic fertilizers, integrated pest management (IPM), conserving water through targeted irrigation techniques, and implementing crop rotation. These not only improve the health of your vineyard but also have positive environmental effects.