“`html
Understanding Insulin Syringe Units
When managing diabetes, it’s crucial to have a solid grasp of how insulin dosage is measured. In this article, we’ll explore the important relationship between milliliters (ml) and units in insulin syringes. Specifically, we’ll clarify that **1 ml is equal to 100 units** in an insulin syringe, which is vital for accurate insulin administration and effective diabetes management.
Insulin Measurements: The Basics
Choosing the right **insulin dosage** is a foundational skill in diabetes management. Understanding insulin measurement is essential for administering the correct amount of medication. **Insulin syringes** are marked in units, with each unit representing a fraction of a milliliter; specifically, **1 ml insulin syringe** contains 100 units of insulin. This means that if your doctor prescribes a certain number of units, converting this measurement to ml could be essential for accurate dosages during injections.
What Is a Unit of Insulin?
A unit of insulin is a measure of the drug’s biological activity. It reflects how much the insulin can lower blood sugar levels. Understanding **units of insulin** helps with correctly measuring and administering **insulin doses**. For instance, a common rule of thumb is to remember that for every 1 ml in an insulin syringe, there are 100 units. This direct conversion simplifies **insulin dosage calculations**, especially for those new to diabetes management.
ML to Units Conversion for Insulin
When you convert ml to units for insulin dosing, it’s crucial for preventing administration errors. Using the **ml to units conversion** guide is critical for anybody administering insulin injections. For instance, if your insulin prescription calls for 50 units, you would simply draw to the 0.5 ml mark on your syringe. **Calculating insulin for diabetics** becomes intuitive upon understanding this 1:100 ratio, easing anxiety about dosing inaccuracies.
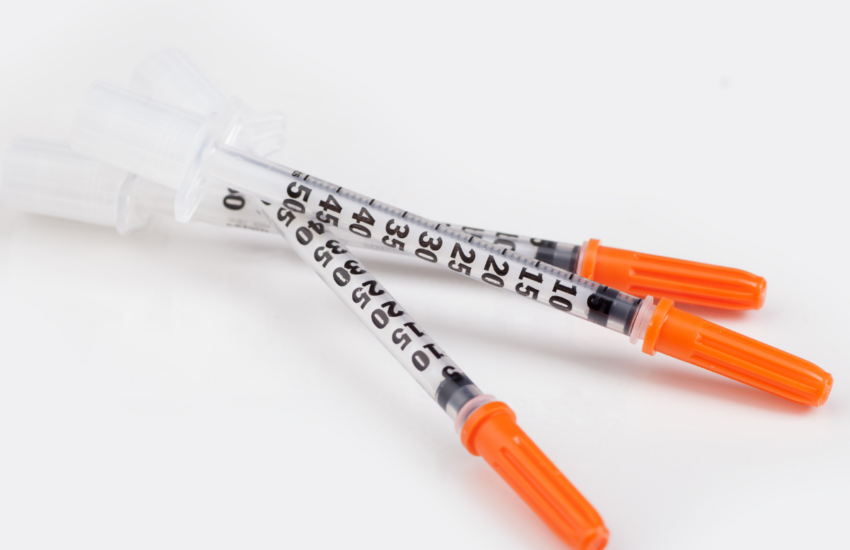
Reading Insulin Syringes Explained
Before injecting insulin, knowing how to properly read the markings on your syringe is fundamental. Insulin syringes have specific calibrations that present **units measurement in syringes**. Typically, syringes come in various sizes, such as 0.3 ml, 0.5 ml, and 1 ml syringes. Knowing how to interpret these markings ensures you’re administering the right dosage. Furthermore, recognizing the differences among **different syringe types** is essential for effective insulin therapy.
Understanding Syringe Markings
Every insulin syringe is calibrated to represent units accurately. Smaller syringes, commonly used for lower doses, will feature markings corresponding to each unit. For example, in a 1 ml insulin syringe, each line may represent 2 units. Moreover, varying **insulin types and dosages** can affect how much insulin is required for each individual scenario. A thorough familiarization with the markings is essential to avoid **insulin errors**, ensuring safe and effective insulin injections.
Proper Insulin Handling Techniques
Once you understand readings and conversions, mastering **insulin injection techniques** boosts safety and effectiveness. Always cleanse the injection area and utilize proper techniques, such as pulling the skin taut or pinching it depending on the injection site. Additionally, if you’re managing type 1 or type 2 diabetes, learning **proper insulin handling** techniques can significantly enhance the ease of administration and optimize **diabetes care strategies**.
Importance of Accurate Insulin Dosage
The effectiveness of insulin therapy heavily relies on **calculating insulin dosages accurately**. Incorrect doses can lead to conditions such as hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia, which can have serious long-term effects. It’s therefore essential to ensure that you’re aware of how to handle dosages concerning the specific needs of your diabetes management plan.
Insulin Therapy Guidelines
Follow established **insulin therapy guidelines** to prevent complications. These guidelines emphasize appropriate dosing, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, and adjustments based on activity, diet, and other medications. For those on insulin therapy, understanding the variation in **insulin types** available and the accompanying dosing recommendations is crucial in minimizing health risks and ensuring stable blood glucose levels.
Avoiding Insulin Delivery Errors
One of the paramount challenges for diabetes patients is to avoid common insulin errors. Under-dosage can lead to persistent elevated **blood sugar levels**, while overdoses may result in acute low blood sugar episodes. Recognizing these potential pitfalls and adhering to prescribed **insulin dosage conversions** can assist in averting serious medical conditions, allowing for a smoother diabetes management experience.
Key Takeaways
- 1 ml of insulin is equal to 100 units in a syringe.
- Understanding insulin syringe measurements and conversions is essential for accuracy.
- Correct reading of syringe markings prevents dosing errors.
- Commit to accurate administration and thorough knowledge of insulin types.
- Follow insulin therapy guidelines for effective management and preventing complications.
FAQ
1. How do I calculate insulin for my diabetes needs?
To calculate insulin, begin with your doctor’s instructions. Using the conversion of 100 units per ml, divide the required units to determine how many milliliters you need. If you require 50 units, draw to the 0.5 ml mark on the syringe. Adjustments may be made based on dietary intake and blood sugar readings.
2. What are the different types of insulin and their dosages?
There are diverse types of insulin, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting varieties. Each has unique timing for onset and how long it lasts. Always work with your healthcare provider to establish an appropriate dosage plan based on the type of insulin you use.
3. Why is it important to learn proper insulin injection techniques?
Proper injection techniques minimize discomfort and reduce the risk of complications such as infections or lipodystrophy. It is essential for effective delivery of insulin and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
4. Can I reuse insulin syringes?
While technically possible, it’s not recommended. Reusing insulin syringes can increase the risk of infection and inaccurate dosing. It’s best practice to use a fresh syringe for each injection to ensure proper dosage and maintain hygiene.
5. How do I store insulin correctly?
Insulin should be stored in a cool place, ideally between 36°F and 46°F (2°C and 8°C). Avoid excessive heat and direct sunlight. Once opened, it can usually be kept at room temperature for up to 28 days, following proper storage guidelines to ensure effectiveness.
6. What to do if I miss an insulin dose?
If you forget to take your insulin, administer it as soon as you remember, unless it’s time for the next dose. Never double dose. Always communicate with your healthcare provider for personalized guideline adjustments based on your situation.
7. How can I avoid insulin-related challenges?
To avoid challenges with insulin administration, create a routine around your injections and inspection of supply levels. Keeping an open line of communication with healthcare professionals for needed adjustments or questions can also facilitate effective management.
“`