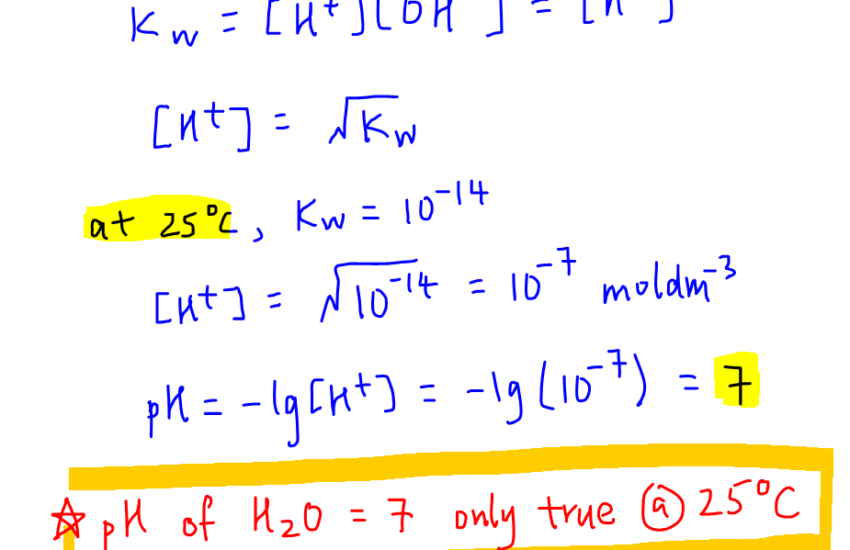Effective Ways to Calculate pH: Master Accurate Measurements in 2025
Understanding how to calculate pH is essential not only in laboratory settings but also in everyday applications ranging from agriculture to environmental science. The pH scale, which quantifies acidity and alkalinity, provides critical insight into various processes, including biological reactions, water quality, and even the fermentation of food. In this article, we will explore multiple pH calculation methods, effective measurement techniques, and their applications across different fields.
Fundamental Concepts of the pH Scale
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, where a pH value of 7 indicates a neutral solution, values below 7 are acidic, and above 7 are alkaline. The relationship between pH and hydrogen ion concentration is logarithmic, meaning that each step from one integer to the next (e.g., from pH 5 to pH 6) represents a tenfold change in acidity. This makes understanding the acidity and alkalinity crucial for suitable applications, from personal health to farming practices.
Understanding pH Values of Common Substances
To further grasp concepts surrounding the pH scale, it’s helpful to know the pH values of common substances. For instance, stomach acid has a pH level between 1.5 and 3.5, while seawater holds a pH around 8. This variation highlights how different environments can exist within the same ecological system and the necessity for precise pH measurement techniques.
Neutral pH and Its Importance
Applied across various domains, achieving neutral pH is considered essential: in biological systems, a neutral pH facilitates optimal enzyme function, while in agriculture, it enhances nutrient availability in soil. Understanding what constitutes neutral pH helps professionals across many fields, aligning their practices to maintain or recover suitable environments.
Factors Influencing pH Levels
Several factors can affect pH including temperature, the presence of salts, and dissolved gases like carbon dioxide. This means that factors affecting pH must be carefully controlled especially in laboratory settings or agricultural practices to ensure purity and consistency of the sample being tested.
Measuring pH Accurately
Accurate pH measurement is pivotal in various scientific fields. Measuring pH accurately not only ensures the purity of water supply but also guarantees optimal conditions for products in food science. Here, we will outline the primary methods to achieve accurate pH readings.
Using pH Meters
One prevalent method for measuring pH is through a pH meter. These devices provide reliable and precise measurements but require calibration with standard buffers prior to use. Calibration ensures the accuracy of readings and minimizes errors common with faulty equipment or inconsistent environmental conditions.
Advantages of pH Test Kits
pH test kits offer an accessible option for non-professionals to measure pH conveniently. These kits typically rely on pH strips or reagents and can be both cost-effective and easy for quick assessments. However, they generally offer less precision compared to digital meters, making them suitable for everyday use but not necessarily laboratory accuracy.
Understanding pH Indicators
pH indicators, another effective measurement method, utilize color changes to indicate pH levels. These materials can be incorporated into experiments or used to verify pH levels visually, making them invaluable for educational purposes, field studies, or casual experimentation in household or community gardening initiatives.
Applications of pH Measurement
pH plays a crucial role in several sectors, from environmental monitoring to pharmaceuticals. Knowing how to properly utilize pH in various fields allows for better product development, environmental health management, and consumer safety.
pH in Environmental Science
Monitoring pH in environmental science is vital for assessing water quality and ecosystem health. Changes in pH can indicate pollution levels, trends in ocean acidification, and shifts in aquatic life viability. For instance, a diminishing pH can adversely impact marine life and disrupt entire ecosystems from coral reefs to coastal fisheries.
The Role of pH in Food Science
In food science, pH significantly affects fermentation processes, preservation, and nutritional profile. For example, maintaining appropriate pH levels in beverages during production is essential to ensuring stability, flavor, and safety. This is particularly notable in products like yogurt, where bacteria thrive within specific pH ranges to generate desired textures and flavors.
pH and Agriculture
Farmers must regularly assess pH levels in soil to optimize crop yield and health. Soil pH directly influences nutrient availability and microbial growth, which consequently affects plant growth and productivity. Methods like adjusting soil pH through * liming * can promote better farming outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding pH through accurate measurements and calculations is crucial across multiple disciplines.
- pH scale variations reflect the acidity of solutions and play a significant role in biological and environmental sciences.
- Various methods exist to measure pH including digital meters, test kits, and indicators, each suited for specific applications.
- The importance of pH extends to agriculture, pharmaceutical development, and food quality control.
- Ongoing pH monitoring is essential for maintaining ecological balances in both natural and artificial environments.
FAQ
1. What are the strongest acids and their pH levels?
Some of the strongest acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, which can have pH levels close to 0. Understanding these extreme measures is critical in fields such as industrial chemistry and lab safety.
2. How does temperature affect pH readings?
Temperature can significantly alter pH readings due to changes in the dissociation constants of acids and bases. It’s essential to account for temperature when performing pH titration techniques and conducting chemical reactions.
3. Can pH levels impact enzyme activity?
Yes, pH can have substantial effects on enzyme activity; changing pH levels can denature enzymes, impacting metabolic pathways and biological processes. This emphasizes the importance of understanding pH in biology and its various applications.
4. What is the effect of acid rain on pH?
Acid rain can lower the pH levels of soil and water bodies, significantly affecting ecosystems and biodiversity. Monitoring these fluctuations is vital for environmental protection efforts and sustainable agriculture.
5. How can pH be adjusted in water systems?
Pipelines and water reservoirs often require pH adjustment to manage acid levels; this can be handled through various aeration and chemical treatment methods to maintain optimal conditions for both human consumption and aquatic life.